Time and effort-saving ideas for busy people
However much you try to slow down and avoid activities that consume time and energy to no purpose, there will still be occasions when you are going to be busy and pressured. That’s a simple fact of modern organizational life. So how to deal with it?
Here are some ideas, taken from a wide range of sources (plus my own experience), that should help you to save time and trouble when things get hectic:
- Always think ahead about the most likely consequences, not just the ones that you want to happen. The idea here is simple: to try to avoid causing yourself more problems and stress through a moment’s thoughtless action. One of the commonest consequences of being under pressure is a failure to look ahead. It seems so important to get a quick result. But cutting corners, taking risks without proper consideration, and rushing into precipitate action can all cost you far more time in cleaning up the mess afterwards than you saved at the time.
- It’s always worth taking ample time to get a message across to others. It’s the same temptation: to rush through some phone call, message, or conversation because you can’t really spare the time and you have so much still waiting for you to do. Resist it! If people can see that you’re harassed, they’ll often try to be helpful by saying they understand when they don’t. Few situations are more maddening than discovering, too late, that someone you were relying on for a key element in a project misunderstood what you said that you wanted.
- Consider every request to attend a meeting with the greatest skepticism. Your default position should be to stay away. Avoid any meeting with no clear agenda, no obvious ending time, and no purpose that makes sense to anyone except the organizer. Don’t assume you can go and quietly do work at the back. It’s more discourteous than staying away and it rarely works.
- Practice at least a dozen firm but polite variations on “no” until you can say them in your sleep. Then use them whenever needed—which will be all the time. The best way to stop yourself becoming overloaded is to refuse to take an anything else. If the person giving you yet more work is your boss, ask for clear priorities, explaining that you need be sure what to drop to make way for the new piece of work. You’ll be surprised how often this will make a boss reconsider.
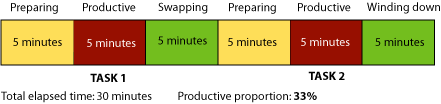
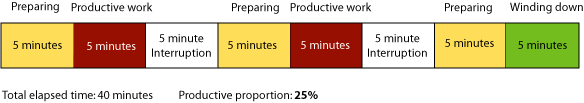
- Learn the two key ways of reading: skimming for relevance and filleting for data. When you skim a document, your sole purpose should be to decide whether it contains anything worth reading. Let your gaze run down the page looking for key words and phrases. If you find any, put a small “x” in the margin and move on. Then glance over the number of “x” markings. Less than 5-6 means don’t mess with it further unless one of those is essential. Filleting is going back to the “x” marks and collecting the data you need. The best way is to make your own notes in a small book. Then toss the original.
- Don’t accept what you’re told on trust, save from proven sources. When you’re rushed, the temptation will be to “save time” by accepting what you’ve been told. Always check. It’s well worth the time. You’ll look an idiot if the information isn’t true, and no one will accept the excuse that you were in a hurry.
- Become familiar with the notions of estimates and orders of magnitude. You can often spot an error or problem almost instantly, without any calculation, by realizing that it is impossible. That’s especially true with numbers. If you know the answer has to be less than 10, and if what is on the page is 14.7, it has to be wrong. No more analysis is needed than that. One of the most useful skills I ever taught myself was the ability to estimate the order of magnitude of the right answer. I rarely needed to know any more to save myself huge amounts of time on analysis.
- Know when to stop. The more you’re under pressure, the more you will be tempted to press on working well beyond the point where your attention and effectiveness begin to fail. Don’t do it. It seems as if it will help, but you’ll most likely either have to do all that work again or waste time clearing up the mess you made for yourself. And you’ll have denied yourself the rest needed even to do that properly.
Coping with turbulence
Imagine someone in a kayak, negotiating a river full of rapids. That’s you, facing all the turbulence and unexpected pressures of your work.An inexperienced and foolish kayaker is totally occupied with trying to deal with every twist and surge of the current. His or her attention is fixed on what is happening right now. The ride is a nightmare of hidden rocks, violent eddies, and constant threats of being overturned and drowned. Time flashes by in a blur of near-panic. Any patches of calm water are used up in exhausted collapse, desperately trying to catch a breath before the next horror.
The more experienced kayaker faces the same perils. But that person has learned to look always a little way ahead, sensing the flow of the river and avoiding some at least of the hidden rocks and shallows. By doing so, he or she has more scope to find areas of slightly calmer water, where rest is possible and there’s a moment to look around and enjoy the view.
Although both kayakers may pass the same time in the rapids, as measured by the clock, the experienced one feels as if he or she has much more time. Time is always as much subjective as objective and when we’re in a turmoil of short-term fire-fighting, it passes with such speed that it causes stress by itself.
If I had to sum all of this up as simply as possible, I would say that the key to coping with stress and pressure is to do just about the opposite of what feels most called for: slow down as much as you can, look ahead as much as possible, drop everything non-essential, and do the rest as carefully and thoughtfully as possible so you only have to do any of it once. And always, always, try to avoid making yet more work for yourself by rushing, cutting corners, and making needless mistakes.
PLEASE NOTE: from August 1st, tomorrow, this blog will leave the Blogger platform and re-surface on Wordpress. I will leave all posts up to that point on Blogger, at the current URL.
New posts will be found from August 1st onwards at http://www.slowleadership.org/blog/
Labels: self-preservation, strategic thinking, stress